The electric vehicle (EV) market is booming globally. Government policies and incentives are accelerating the adoption of EVs. Battery technology advancements are improving EV performance and affordability. As more people switch to electric vehicles, the need for reliable and efficient charging stations is growing rapidly. Investing in EV charging stations has become an attractive opportunity. This article explores the market trends, potential returns, and future outlook to help investors make informed decisions.
Market Overview of Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations
Global Growth Trend of the EV Market
The global electric vehicle market has shown a robust growth trend. In 2024, the market size of electric vehicles was estimated to reach $1,328.08 billion, and it is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.5% from 2025 to 2030. Government policies and incentives have accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles worldwide. Many countries have implemented strict emission regulations and provided incentives such as subsidies and tax breaks for consumers and manufacturers, encouraging the shift from internal combustion engine vehicles to electric alternatives

[Global EV Market Size2024-2030 ]
Advancements in battery technology have significantly improved the driving range, performance, and affordability of electric vehicles. Improvements in solid-state batteries and lithium-ion batteries have reduced costs and increased energy density, making electric vehicles more appealing to consumers. Additionally, the expansion of the transportation and logistics industry has significantly boosted the demand for electric vehicles. With the continuous growth of global trade and e-commerce, the demand for efficient and sustainable transportation solutions has increased. Electric vehicles offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines due to their lower emissions and lower operating costs. Especially in urban areas, with the increase in delivery services and the need to reduce air pollution, logistics companies are increasingly integrating electric vans and trucks into their fleets.
[Statistics from Global Electric Vehicle Outlook Report 2025-International Energy Agency IEA]
Growth Trends of the EV Market in Major Regions
Europe
The European EV charging station market has expanded through government initiatives, especially the European Green Deal, which focuses on reducing emissions and promoting sustainable transportation. China, the world’s largest EV market, continues to maintain its dominant position in the Asia-Pacific region through infrastructure investment and charging coverage. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China reported that more than 1.8 million charging stations have been installed nationwide, with plans to build 20 million charging points by 2025
North America
In North America, the U.S. EV charging station market was valued at $400 million, $500 million, and $700 million in 2022, 2023, and 2024 respectively, supported by federal funding programs such as the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program, which allocates $5 billion to each state to build an interconnected ecosystem of EV charging stations. The U.S. Department of Transportation has confirmed an allocation of $7.5 billion for the construction of a national network of 500,000 EV chargers.
Middle East
The “Belt and Road” Initiative is boosting the development of the electric vehicle market in countries along the route. China aims to build 20 million charging points by 2025 and is exporting its EV and charging technology to other “Belt and Road” countries. In the Middle East, Saudi Arabia is reducing EV import tariffs and exempting purchase and registration fees, aiming to deploy over 5,000 public charging points by 2026 to form an integrated “city + commuting + tourism” layout. The UAE plans to increase the proportion of electric and hybrid vehicles to 50% by 2050 and has currently deployed over 700 public charging points to support the local EV market.
Market Landscape of EV Charging Stations
In 2024, the EV charging station industry was valued at $39.7 billion, and the market size of DC charging is expected to exceed $180.5 billion by 2034. Currently, the public EV charging station segment accounts for more than 87% of the market share and is expected to grow at a rate of over 26% by 2034. The market is shifting towards DC fast charging, especially for highways and commercial use where long-distance travel and efficient charging capabilities are required. The deployment of DC fast-charging stations is increasing rapidly globally. For example, in the UK, fast chargers can charge an electric vehicle to 80% in approximately 20 – 30 minutes. Despite the higher construction costs of DC charging stations due to configuration, cooling preparation investment, and more advanced grid integration technology, market demand remains strong.
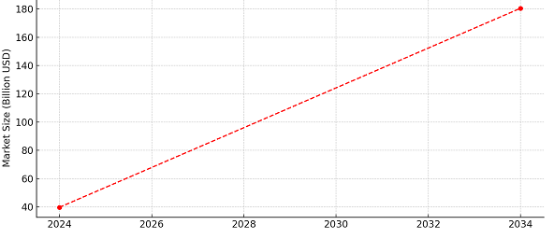
[Global DC Charging Station Market Size(2024 -2034)]
The Close Link between the EV Market and the Demand for Charging Stations
There is a close link between the growth of the electric vehicle market and the demand for charging stations. As the number of electric vehicles in use increases, the demand for charging stations will inevitably grow. According to a 2020 report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), China accounts for 53% of the world’s slow chargers and 83% of fast chargers. In 2022, the public charger application segment accounted for approximately 87% of the market share, and the DC charging station segment captured about 74% of the revenue share. With the increase in electric vehicle sales and the growing demand for zero-emission transportation, the demand for the EV charging station market will be further enhanced.
Government policies and incentives
Europe
The European Commission has proposed the “Fit for 55” package, aiming to increase the share of renewable energy in the energy mix from 55% to 60% by 2030 and to 69% by 2035. The EU Renewable Energy Directive, which came into effect in 2022, will further expand the scale of renewable energy power used by electric vehicles, enhancing their environmental benefits and market attractiveness.
The European Commission and the European Investment Bank plan to provide 10 billion euros in public funds by 2027 for green investments, including electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These funds will be provided in the form of loans, guarantees, and blended financing instruments to attract more private investment, accelerate the construction of charging infrastructure, and improve the coverage and service capacity of charging facilities.
North America
The United States, through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), supports the deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. It offers consumers a tax credit of up to $7,500 per vehicle until 2032. Additionally, it provides a 30% tax credit for the cost of certain alternative fuel vehicle refueling facilities, including electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These incentives reduce investment costs, enhance the return on investment, and drive the construction and development of charging stations.
The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law in the U.S. promotes the domestic production and installation of charging infrastructure, providing policy support and financial guarantees for charging station construction. This helps to increase the supply and coverage of charging stations.
Middle East
In the United Arab Emirates, the Dubai Municipality requires that 5% of parking spaces in new buildings be reserved for green or low-emission vehicles. It also stipulates specific electricity prices for electric vehicle charging stations, uniformly implemented by the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority. Additionally, it offers incentives such as free parking, exemption from tolls, and reduced registration fees to promote the use of electric vehicles.
Saudi Arabia, through its sovereign wealth fund, the Public Investment Fund (PIF), has made several high-profile investments. For example, in 2023, the PIF established a joint venture, Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Company (EVIQ), with the Saudi Electricity Company, planning to install more than 5,000 fast chargers in Saudi Arabia by 2030, driving the construction and development of local charging infrastructure.
Investment Cost Analysis of EV Charging Stations
Initial Investment Costs
Equipment Procurement:
The prices of charging equipment vary significantly based on brand and power.
In North America, for instance, a 7 – 22kW slow – charging station from a well – known local brand might cost around $1,000−3,000, while a 60 – 120kW fast – charging station could range from$10,000−30,000.
In Europe, some high – end fast – charging equipment with advanced features may be even more expensive. However, certain emerging brands from other regions offer cost – effective alternatives, with prices 20% – 30% lower than local leading brands.
Mid-power DC chargers (30-60kW) offer optimal ROI for urban sites. For example, chinese brand like Olink, Olink‘s 30kW DC charger station costs 40% per unit, less than European and American brands, with modular design allowing future upgrades to 60kW. Its compact size (0.8㎡footprint) suits space-constrained locations like parking garages.
Site Rental or Purchase
In prime urban areas of North America, such as New York City, rentinga site suitable for a medium – sized charging station (accommodating 10 – 20 charging stations) can cost $30,000−80,000 annually.
In Europe, in cities like London, the rental cost may be even higher.
In the Middle East, in cities like Dubai, land prices are high, but some government – designated areas offer more affordable rental options for charging station projects.
Infrastructure Construction
Power capacity expansion is a major expense.
In North America, upgrading the power grid to support a 10 – charging – pile station with high – power chargers might cost 20,000−50,000.
In Europe, due to differences in grid infrastructure and regulations, the cost can vary from 30,000−60,000. The cost of laying cables and other infrastructure also depends on the site’s location and complexity, usually ranging from 10,000−30,000.
Operational Costs
Electricity Expenditure: In North America, electricity prices for commercial use vary by region and time of day. In some areas, peak – hour electricity prices can reach 0.2−0.3 per kWh, while off – peak prices may be as low as 0.08−0.15 per kWh. In Europe, electricity costs also show significant regional differences, with some countries having relatively high prices. In the Middle East, electricity prices are generally more stable, but still, different tariffs apply to charging stations.
Equipment Maintenance and Repair: Regular maintenance of charging equipment is essential. In North America, annual maintenance costs for a medium – sized station can be around 5,000−10,000, covering inspection, software updates, and replacement of worn – out parts. In Europe, due to higher labor costs in some regions, the maintenance cost may be 10% – 20% higher.
Personnel Management Costs: Staffing requirements for a charging station include operators, technicians, and administrative personnel. In North America, employing a small team to manage a medium – sized station can cost 50,000−80,000 per year. In Europe, this cost can be even higher in some countries with high minimum wage standards.
Cost Structure Differences among Different – Scale and – Type Charging Stations
For small – scale community charging stations with mainly slow – charging stations (5 – 10 piles), the initial investment is relatively low, mainly concentrated on equipment and site rental. The operational cost is dominated by electricity and minimal maintenance. In contrast, large – scale high – power fast – charging stations on highways or in commercial areas require a large amount of initial investment in high – power charging equipment, significant power capacity expansion, and better – equipped infrastructure. Their operational costs are also high, with high – volume electricity consumption and more frequent equipment maintenance needs. Public charging stations, which need to be accessible at all times, often require more personnel management compared to private or semi – private charging stations in specific complexes.
In conclusion, the cost of investing in EV charging stations globally varies greatly depending on multiple factors. However, with the continuous growth of the EV market, appropriate cost – control measures and business models can still make such investments potentially profitable.
Revenue Streams of EV Charging Stations
Direct Charging Fees (Pay-per-Use)
The primary income for most EV charging stations comes from charging service fees, either by kWh, time, or session. In Europe, average public DC fast charging prices range from €0.40–€0.79/kWh (Source: Transport & Environment, 2024). Pricing is influenced by location, time of day, and power level.
Membership & Subscription Plans
Operators often offer monthly subscriptions or loyalty packages to encourage frequent use. These plans generate recurring revenue and improve customer retention. For example, in North America, plans like Electrify America’s Pass+ charge $4/month for discounted rates and priority access.
Advertising & Digital Displays
High-traffic charging stations can earn 10–15% of income from digital out-of-home ads, leveraging the 15–45 minute dwell time of EV drivers.
Retail Partnerships & On-site Services
EV charging is increasingly co-located with retail sites, boosting customer dwell time and enabling lease or revenue-sharing models. For example, over 60% of new UK chargers are installed at retail locations.
Risks and Challenges of EV Charging Station Investment
Market competition and demand fluctuations
Despite the increasing number of players in the global charging station market, the rapid growth of electric vehicle ownership brings a lot of space.In the long run, policies in developed regions such as Europe and the United States continue to promote the transformation of electrification, and the demand in emerging markets in the Middle East is growing explosively, reserving sufficient market opportunities for new entrants.
Technology iteration and device renewal
Although the development of new technologies has brought pressure to update equipment, the industry has formed compatible standards. Existing equipment can be upgraded modularly to extend the service life, and most companies invest in R&D to reduce costs. New investors can use mature technology solutions to avoid early-stage technology risks and quickly integrate into the market.
Changes in policies and regulations
Government support remains a key driver for charging infrastructure, shifting from upfront subsidies to long-term mechanisms like operational support. Improved regulations raise entry barriers but help stabilize the market and protect compliant investors’ long-term returns.
Cost vs. benefit uncertainty
Although the initial investment and operating costs need to be carefully planned, many governments have reduced the financial pressure through tax breaks and low-interest loans. With the advancement of technology, equipment prices are on a downward trend, scale effects are gradually emerging, and the long-term revenue potential far exceeds the short-term cost pressure.
Success Cases Studies
ChargePoint
As a leading EV charging network operator in North America, ChargePoint delivered strong results from 2020 to 2024: Hardware and service fees: ChargePoint sells charging equipment and offers installation and maintenance services to businesses and individuals, earning revenue from hardware sales and services.
Network operation income:Through its charging network, ChargePoint charges users for charging services and shares revenue with charging station owners. This has helped it build a large charging network and capture a significant market share.
Partner relationships: ChargePoint has established partnerships with automakers and energy firms. These partnerships enhance its resource base and drive business growth.
IONITY
From 2020 to 2024, IONITY, backed by BMW, Daimler, Ford, and other automakers, constructed high – power fast – charging stations on European highways, with the following profit – making points:
Cross – brand compatibility: IONITY’s charging stations are compatible with various EV brands and models, attracting numerous users and generating revenue from charging fees.
Strategic location: The charging stations are located on major highways, providing convenient charging for long – distance EV travel and increasing usage frequency and revenue opportunities.
Collaboration with automakers: IONITY cooperates with BMW and Mercedes – Benz to offer exclusive charging services for their EV owners. This expands its user base and market share with the support and promotion of automakers.
Future Trends of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Technological Innovation Driving Industry Upgrades
Ultra – fast Charging Technology Becoming Mainstream
In the future, ultra – fast charging technology will become widespread, greatly shortening charging time and enhancing user experience. As pointed out by Huawei Digital Power, in 2024, many cities are accelerating the construction of “ultra – fast charging networks”. The scale of ultra – fast charging stations in cities like Shenzhen and Chongqing has already exceeded 1,000. It is estimated that by 2028, the coverage of ultra – fast charging networks will surpass that of gas stations comprehensively, and 70% of existing integrated charging stations are expected to be phased out.
Application of Power Pooling Technology
Power pooling technology enables power sharing among parking spaces, improves the utilization rate of municipal electricity, and meets the charging needs of different vehicle models. It also reduces the cost of building charging stations, such as a 40% reduction in municipal electricity expansion costs and a 20% reduction in cable costs, while supporting the evolution from fast charging to ultra – fast charging in the future.
Advantages of Full – Liquid – Cooled Architecture
The full – liquid – cooled architecture features high protection levels, efficient heat dissipation, and dust – free operation. It can adapt to harsh environments such as high temperatures, high corrosion, and dusty conditions, extending the lifespan of charging stations and improving their reliability.Leading manufacturers are adopting liquid-cooled tech to extend equipment lifespan.For example, Like Olink’s 30kW DC charger station implements IP65-rated liquid cooling, maintaining 55°C optimal temperature in desert climates (tested in UAE projects), reducing failure rates by 35% compared to air-cooled models.
Continuous Growth in Market Demand
Increasing Number of Electric Vehicles: The global electric vehicle market is projected to reach 13280.8 billion US dollars in 2024 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 32.5% from 2025 to 2030. The rise in the number of electric vehicles will directly drive demand for charging stations.
Expanding Application Scenarios: In addition to private cars, ultra – fast charging technology will accelerate the electrification of commercial vehicles such as logistics vehicles, further expanding the market demand for charging stations.
New Opportunities Brought by Business Model Innovation
Integration of Photovoltaic, Energy Storage and Charging: Photovoltaic, energy storage and charging integrated charging stations can reduce grid impact and enable a business model of charging at low electricity prices and discharging at high prices for faster profitability. According to Huawei Digital Power, future photovoltaic, energy storage and charging stations will evolve from “multiple cabinet patchworks” to “intelligent integration,” offering investors more promising business opportunities.
Promotion of V2G Technology: V2G technology enables interaction between electric vehicles and the grid. Vehicle owners can feed electricity back into the grid during peak electricity demand periods for additional income while lowering their own charging costs. As pilot programs expand, V2G is expected to become a new growth point for charging station profitability.
Policy Support and Standardization
Government Policies Accelerating Infrastructure Development
Global governments are actively promoting the deployment of EV charging infrastructure through supportive policies, subsidies, and strategic plans. In the European Union, the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR), enforced from April 2024, mandates that fast EV charging stations (≥150 kW) be installed every 60 km along core transport corridors by 2025. Similarly, China’s 14th Five-Year Plan includes targeted goals to deploy over 20 million EV chargers by 2025, backed by local government subsidies and grid upgrade programs. These policies not only reduce the investment threshold but also ensure long-term policy stability for charging station investors.
Financial Incentives and Public Funding
Many countries offer financial incentives for charging station deployment. For instance, Germany’s KfW 441 program provides up to €900 per charging point for businesses, while the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act allocates $7.5 billion for nationwide EV charging networks. These public investments significantly lower the capital risk for private investors and help accelerate the return on investment (ROI) for charging projects.
Push for Technical Standardization and Interoperability
Standardization is crucial for ensuring safety, compatibility, and scalability of EV charging infrastructure. Organizations such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) are actively developing unified standards for connector types (e.g., CCS2 in Europe, GB/T in China), charging protocols (e.g., OCPP 2.0.1), and V2G communication standards. The EU’s AFIR also enforces mandatory payment interoperability, requiring every fast charging station to accept contactless card payments to improve user accessibility and station utilization.
Support for V2G and Renewable Integration Standards
To encourage grid-interactive charging infrastructure, policies are being introduced to support V2G integration. In Japan, the government has included V2G communication standards (ISO 15118) in pilot projects and aims for commercial-scale rollouts by 2030. Similarly, China’s State Grid has launched demonstration zones that integrate V2G + solar + storage, with clear technical guidance and operational standards emerging to attract investment and ensure secure operation
Industry Consolidation and Increased Market Concentration
Leading Enterprises’ Advantages Expand: As market competition intensifies, leading enterprises with technological, brand, and operational strengths will see their market shares grow. In China, enterprises like TELD and StarCharge already hold significant shares in the charging station operation market and are expected to maintain their leading positions.
More Cross – Industry Collaborations: Car manufacturers, energy companies, tech firms, etc., will strengthen cooperation to jointly promote the construction and development of charging stations. For example, IONITY, a joint venture of BMW, Daimler, Ford, and other automakers, has built numerous high – power fast – charging stations along European highways.
Conclusion
Investing in EV charging stations is highly promising. The EV market is booming, with a CAGR of 32.5% expected from 2025 to 2030. Government policies worldwide are strongly supportive, offering subsidies and tax incentives to accelerate the shift to electric mobility. Technological advancements are reducing costs and enhancing charging efficiency. While challenges like market competition and technology updates exist, they are outweighed by the opportunities. The growing demand for sustainable transport, coupled with innovative business models like V2G and photovoltaic integration, opens new avenues for profitability. Successful case studies demonstrate the viability and strong returns of well – planned charging station investments. For investors seeking to capitalize on the green energy transition and benefit from long – term growth, EV charging stations are an attractive and timely opportunity.


